Big Blue Blog - Fabric Test Methods
 BlogCleanroom13.01.2022
BlogCleanroom13.01.2022
In order to assess the suitability of fabrics for different contamination control systems it is necessary to test a range of performance characteristics both of the material itself and also of garments constructed from the fabric.
A variety of standard tests can be used to assess factors affecting contamination control and wearer comfort and to give a direct comparison of different fabrics.
The following list gives examples of useful test methods; however, different National Standards and tests are used by different fabric manufacturers.
It is therefore recommended that when selecting cleanroom fabrics, samples are subjected to the same test methods, preferably carrier out by the same test house at the same time, to obtain directly comparable results.
Fabric pore size
BS 3321 Method for measurement of the equivalent pore size of fabrics.
The bubble point test is used to establish the size of the pores which pass through the fabric from one side to the other. Pore size results from the tightness and accuracy of the weave.
Decreasing pore size gives greater particle hold out and therefore better filtration but also decreases the ability of the fabric to transmit air and water vapour and therefore reduces wearer comfort.
For a filament polyester fabric the pore diameter will typically be around 18 micrometres or less.
As a comparison a polycotton fabric will have a pore size of approximately 65 micrometres.
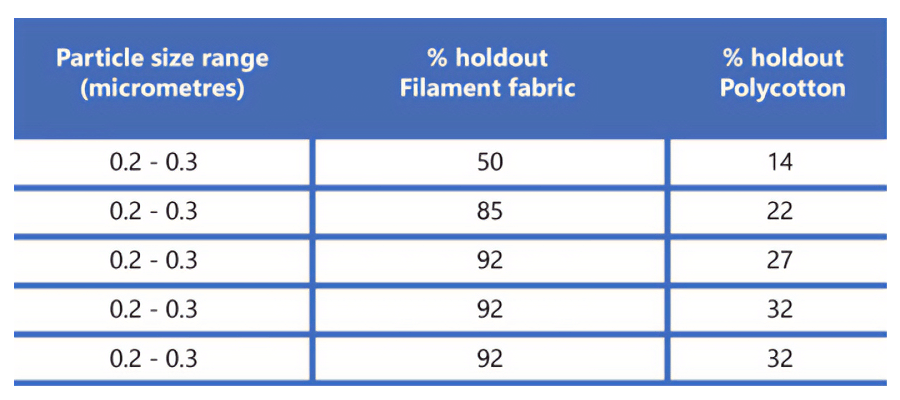
Particle holdout efficiency
British Textile Technology Group (BTTG) Particle Barrier Efficiency (Shirley method 22).
A direct particle challenge test is used to estimate the number of particles of different sizes filtered out by the fabric.
The fabric is subjected to an airstream containing a known number of particles with a range of sizes. The number of particles passing through the material is measured and the percentage of particles filtered out by the fabric can be calculated. This is reported for each particle size as a percentage holdout.
A typical woven high-grade filament fabric and polycotton will produce the following results.
Dry linting propensity
BS 6909 1988. Method for generation and counting of the airborne linting propensity of fabrics in the dry state.
This test examines the numbers of particles generated by the fabric itself whilst undergoing a standard flexing under mild abrasion.
Water vapour permeability
ASTM E96. Standard test methods for water vapour transmission of materials.
This test is used to establish the rate at which water vapour will pass through the fabric and is measured in grams per square metre of test fabric per hour. A high-grade barrier fabric will typically give a result of 20 grams per square metre of fabric per hour. Polycotton fabric will be approximately 28 grams per square metre of fabric per hour.
This test gives an indication of garment comfort as the faster moisture vapour can disperse from the skin surface the more comfortable the wearer feels.
This test gives an indication of garment comfort as the faster moisture vapour can disperse from the skin surface the more comfortable the wearer feels.
Air permeability
BS EN ISO 9237. Textiles. Determination of the permeability of fabrics of air.
This test method is used to assess the rate at which air can pass through the fabric and gives a further indication of wearer comfort.
The results are obtained in litres of air per square metre of test fabric per second at 0.98 mb pressure differential.
A typical result for a woven filament barrier fabric would be about 45 litres of air per square metre of test fabric per second and for polycotton approximately 170 litres of air/square metre of test fabric per second.
If air can pass easily through the fabric then the body temperature of the wearer is more readily adjusted resulting in a more comfortable garment.
Static dissipation behaviour
BS EN 1149. Protective clothing, Electrostatic properties. Test method for measurement of surface resistivity.
Gives details of tests to investigate the electro-static dissipative properties of fabrics.
Abrasion resistance
BS EN 530. Abrasion resistance of protective clothing material.
This test gives an indication of the likely wear characteristics of the fabric over time.
